Below is a detailed account of the Civil Aeronautics Board’s Aircraft Accident Report regarding the plane crash that occurred on February 3, 1959, near Mason City, Iowa
This tragic incident is often referred to as “The Day the Music Died” because it claimed the lives of rock and roll musicians Buddy Holly, Ritchie Valens (Richard Valenzuela), and J.P. Richardson, also known as the Big Bopper.
The Civil Aeronautics Board Report
Full text of the Civil Aeronautics Board Aircraft Accident Report on the plane crash that killed Buddy Holly, Ritchie Valens and the Big Bopper
This is the Crash Report
Aircraft Accident Report
Adopted: September 15, 1959
Released September 23, 1959 Mason City, Iowa
February 3, 1959
Synopsis
A Beech Bonanza, N 3794N, crashed at night approximately 5 miles northwest of the Mason City Municipal Airport, Mason City, Iowa, at approximately 0100, February 3, 1959. The pilot and three passengers were killed and the aircraft was demolished.The aircraft was observed to take off toward the south in a normal manner, turn and climb to an estimated altitude of 800 feet, and then head in a northwesterly direction. When approximately 5 miles had been traversed, the tail light of the aircraft was seen to descend gradually until it disappeared from sight. Following this, many unsuccessful attempts were made to contact the aircraft by radio. The wreckage was found in a filed later that morning.
This accident, like so many before it, was caused by the pilot’s decision to undertake a flight in which the likelihood of encountering instrument conditions existed, in the mistaken belief that he could cope with en route instrument weather conditions, without having the necessary familiarization with the instruments in the aircraft and without being properly certificated to fly solely by instruments.
Investigation
Charles Hardin, J.P. Richardson, and Richard Valenzuela were members of a group of entertainers appearing in Clear Lake, Iowa, the night of Feb. 2, 1959. The following night they were to appear in Moorhead, Minnesota. Because of bus trouble, which had plagued the group, these three decided to go to Moorhead ahead of the others. Accordingly, arrangements were made through Roger Peterson of the Dwyer Flying Service, Inc., located on the Mason City Airport, to charter an aircraft to fly to Fargo, North Dakota, the nearest airport to Moorhead.
At approximately 1730,* Pilot Peterson went to the Air Traffic Communications Station (ATCS), which was located in a tower on top of the Administration Building, to obtain the necessary weather information pertinent to the flight. This included the current weather at Mason City, Iowa; Minneapolis, Redwood Falls, and Alexandria, Minnesota and the terminal forecast for Fargo, North Dakota. He was advised by the communicator that all these stations were reporting ceilings of 5,000 feet or better and visibility of 10 miles or above; also, that the Fargo terminal forecast indicated the possibility of light snow showers after 0200 and a cold frontal passage about 0400. The communicator told Peterson that a later terminal forecast would be available at 2300. At 2200 and again at 2330 Pilot Peterson called ATCS concerning the weather. At the latter time he was advised that the stations en route were reporting ceilings of 4200 feet or better with visibility still 10 miles or greater. Light snow was reported at Minneapolis. The cold front previously reported by the communicator as forecast to pass Fargo at 0400 was now reported to pass there at 0200. The Mason City weather was reported to the pilot as: ceiling measured 6,000 overcast; visibility 15 miles plus; temperature 15 degrees; dew point 8 degrees; wind south 25 to 32 knots; altimeter setting 29.96 inches.
At 2355, Peterson, accompanied by Hubert Dwyer, a certificated commercial pilot, the local fixed-base operator at the Mason City Airport, and owner of Bonanza N3794N (the aircraft used on the flight), again went to ATCS for the latest weather information. The local weather had changed somewhat in that the ceiling had lowered to 5,000 feet, light snow was falling, and the altimeter setting was now 29.90 inches.
The passengers arrived at the airport about 0040 and after their baggage had been properly stowed on board, the pilot and passengers boarded the aircraft. Pilot Peterson told Mr. Dwyer that he would file his flight plan by radio when airborne. While the aircraft was being taxied to the end of runway 17, Peterson called ATCS and asked for the latest local and en route weather. This was given him as not having changed materially en route; however, the local weather was now reported as: Precipitation ceiling 3,000 feet, sky obscured; visibility 6 miles; light snow; wind south 20 knots, gusts to 30 knots; altimeter setting 29.85 inches.

A normal takeoff was made at 055 and the aircraft was observed to make a left 180-degree turn and climb to approximately 800 feet and then, after passing the airport to the east, to head in a northwesterly direction. Through most of the flight the tail light of the aircraft was plainly visible to Mr. Dwyer, who was watching from a platform outside the tower. When about five miles from the airport, Dwyer saw the tail light of the aircraft gradually descend until out of sight. When Peterson did not report his flight plan by radio soon after takeoff, the communicator, at Mr. Dwyer’s request, repeatedly tried to reach him but was unable to do so. The time was approximately 0100.
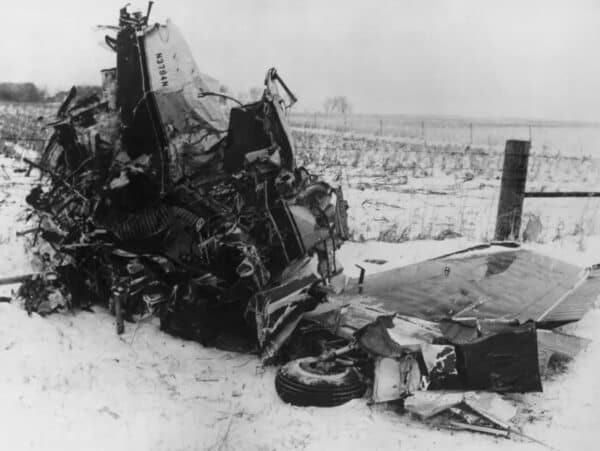
After an extensive air search, the wreckage of N 3794N was sighted in an open farm field at approximately 0935 that morning. All occupants were dead and the aircraft was demolished. The field in which the aircraft was found was level and covered with about four inches of snow.
The accident occurred in a sparsely inhabited area and there were not witnesses. Examination of the wreckage indicated that the first impact with the ground was made by the right wing tip when the aircraft was in a steep right bank and in a nose-low attitude. It was further determined that the aircraft was traveling at high speed on a heading of 315 degrees. Parts were scattered over a distance of 540 feet, at the end of which the main wreckage was found lying against a barbed wire fence. The three passengers were thrown clear of the wreckage, the pilot was found in the cockpit. The two front seat safety belts and the middle ones of the rear seat were torn free fro their attach points. The two rear outside belt ends remained attached to their respective fittings; the buckle of one was broken. None of the webbing was broken and no belts were about the occupants.
Although the aircraft was badly damaged, certain important facts were determined. There was no fire. All components were accounted fro at the wreckage site. There was no evidence of inflight structural failure or failure of the controls. The landing gear was retracted at the time of impact. The damaged engine was dismantled and examined; there was no evidence of engine malfunctioning or failure in flight. Both blades of the propeller were broken at the hub, giving evidence that the engine was producing power when ground impact occurred. The hub pitch-change mechanisms indicated that the blade pitch was in the cruise range.
Despite the damage to the cockpit the following readings were obtained:
Magneto switches were both in the “off” position.
Battery and generator switches were in the “on” position.
The tachometer r.p.m. needle was stuck at 2200.
Fuel pressure, oil temperature and pressure gauges were stuck in the normal or green range.
The attitude gyro indicator was stuck in a manner indicative of a 90-degree angle.
The rate of climb indicator was stuck at 3,000-feet-per-minute descent.
The airspeed indicator needle was stuck between 165-170 mph.
The directional gyro was caged.
The omni selector was positioned at 114.9, the frequency of the Mason City omni range.
The course selector indicated a 360-degree course.
The transmitter was tuned to 122.1, the frequency for Mason City.
The transmitter was tuned to 122.1, the frequency for Mason City.
The Lear autopilot was not operable.
The Aircraft
The aircraft, a Beech Bonanza, model 35, S/N-1019, identification N 3794N, was manufactured October 17, 1947. It was powered by a Continental model E185-8 engine which had a total of 40 hours since major overhaul. The aircraft was purchased by the Dwyer Flying Service, July 1, 1958, and, according to records and the testimony of the licensed mechanic employed by Dwyer, had been properly maintained since its acquisition. N 3794N was equipped with high and low frequency radio transmitters and receivers, a Narca omnigator, Lear autopilot (only recently installed and not operable), all the necessary engine and navigational instruments, and a full panel of instruments used for instrument flying, including a Sperry F3 attitude Gyro.
Pilot
Roger Arthur Peters, 21 years old, was regularly employed by Dwyer Flying Service as a commercial pilot and flight instructor, and had been with them bout one year. He had been flying since October of 1954, and had accumulated 711 flying hours, of which 128 were in Bonanza aircraft. Almost all of the Bonanza time was acquired during charter flights. He had approximately 52 hours of dual instrument training and had passed his instrument written examination. He fail an instrument flight check on March 21, 1958, nine months prior to the accident. His last CAA second-class physical examination was taken March 29, 1958. A hearing deficiency of his right Ear was found and because of this he was given a flight test. A waiver noting this hearing deficiency was issued November 29, 1958. According to his associates, he was a young married man who built his life around flying. When his instrument training was taken, several aircraft were used and these were all equipped with the conventional type artificial horizon and none with the Sperry Attitude Gyro such as was installed in Bonanza N 3794N. These two instruments differ greatly in their pictorial display.
The conventional artificial horizon provides a direct reading indication of the bank and pitch attitude of the aircraft which is accurately indicated by a miniature aircraft pictorially displayed against a horizon bar and as if observed from the rear.. The Sperry F3 gyro also provides a direct reading indication of the bank and pitch attitude of the aircraft, but its pictorial presentation is achieved by using a stabilized sphere whose free-floating movements behind a miniature aircraft presents pitch information with a sensing exactly opposite from that depicted by the conventional artificial horizon.
The Weather
The surface weather chart for 0000 February 3, 1959, showed a cold front extending from he northwestern corner of Minnesota through central Nebraska with a secondary cold front through North Dakota. Widespread snow shower activity was indicated in advance of these fronts. Temperatures along the airway route form Mason City to Fargo were below freezing at all levels with an inversion between 3,000 and 4,000 feet and abundant moisture present at all levels through 12,000 feet. The temperature and moisture content was such that moderate to heavy icing and precipitation existed in the clouds along the route. Winds aloft along the route at altitudes below 10,000 feet were reported to be 30 to 50 knots from southwesterly direction, with the he strongest winds indicated to be closest to the cold front.
A flash advisory issued by the U.S. Weather Bureau at Minneapolis at 2335 on February 2 contained the following information: “Flash Advisory No. 5 A band of snow about 100 miles wide at 2335 from extreme northwestern Minnesota, northern North Dakota through Bismarck and south-southwestward through Black Hills of South Dakota with visibility generally below 2 miles in snow. This area or band moving southeastward about 25 knots. cold front at 2335 from vicinity Winnipeg through Minot, Williston, moving southeastward 25 to 30 knots with surface winds following front north-northwest with 25 to gusts of 45. Valid until 0335.” Another advisory issued by the U. S. Weather Bureau at Kansas City, Missouri at 0015 on February 3 was: “Flash Advisory No. 1. Over eastern half of Kansas ceilings are locally below one thousand feet, visibilities locally 2 miles or less in freezing drizzle, light snow and fog. Moderate to locally heavy icing areas of freezing drizzle and locally moderate icing in clouds below 10,000 feet over eastern portion Nebraska, Kansas, northwest Missouri and most of Iowa. Valid until 0515.” Neither communicator could recall having drawn these flash advisories to the attention of Pilot Peterson. Mr. Dwyer said that when he accompanied pilot Peterson to ATCS, no information was given them indicating instrument flying weather would be encountered along the route.
Analysis
There is no evidence to indicate that very important flash advisories regarding adverse weather conditions were drawn to the attention of the pilot. On the contrary, there is evidence that the weather briefing consisted solely of the reading of current weather at en route terminal and terminal forecasts for the destination. Failure of the communicators to draw these advisories to the attention of the pilot and to emphasize their importance could readily lead the pilot to underestimate the severity of the weather situation.
It must be pointed out that the communicators’ responsibility with respect to furnishing weather information to pilots is to give them all the available information, to interpret this data if requested, but not to advise in any manner. Also, the pilot and the operator in this case had a definite responsibility to request and obtain all of the available information and to interpret it correctly.
Mr. Dwyer said that he had confidence in Peterson and relied entirely on his operational judgment with respect to the planning and conduct of the flight.
At Mason City, at the time of takeoff, the barometer was falling, the ceiling and visibility were lowering, light snow had begun to fall, and the surface winds and winds aloft were so high one could reasonably have expected to encounter adverse weather during the estimated two-hour flight.
It was already snowing at Minneapolis, and the general forecast for the area along the intended route indicated deteriorating weather conditions. Considering all of these facts and the fact that the company was certificated to fly in accordance with visual flight rules only, both day and night, together with the pilot’s unproved ability to fly by instrument, the decision to go seems most imprudent.
It is believe that shortly after takeoff pilot Peterson entered an area of complete darkness and one in which there was no definite horizon; that the snow conditions and the lack of horizon required him to rely solely on flight instruments for aircraft attitude and orientation.
The high gusty winds and the attendant turbulence which existed this night would have caused the rate of climb indicator and the turn and bank indicator to fluctuate to such an extent that an interpretation of these instruments so far as attitude control is concerned would have been difficult to a pilot as inexperienced as Peterson. The airspeed and altimeter alone would not have provided him with sufficient reference to maintain control of the pitch attitude. With his limited experience the pilot would tend to rely on the attitude gyro which is relatively stable under these conditions.
Service experience with the use of the attitude gyro has clearly indicated confusion among pilots during the transition period or when alternating between conventional and attitude gyros. Since Peterson had received his instrument training in aircraft equipped with the conventional type artificial horizon, and since this instrument and the attitude gyro are opposite in their pictorial display of the pitch attitude, it is probably that the reverse sensing would at times produce reverse control action. This is especially true of instrument flight conditions requiring a high degree of concentration or requiring multiple function, as would be the case when flying instrument conditions in turbulence without a copilot. The directional gyro was found caged and it is possible that it was never used during the short flight. However, this evidence is not conclusive. If the directional gyro were caged throughout the flight this could only have added to the pilot’s confusion.
Conclusion
At night, with an overcast sky, snow falling, no definite horizon, and a proposed flight over a sparsely settled area with an absence of ground lights, a requirement for control of the aircraft solely by reference to flight instruments can be predicated with virtual certainty.
The Board concludes that pilot Peterson, when a short distance from the airport, was confronted with this situation. Because of fluctuation of the rate instruments caused by gusty winds he would have been forced to concentrate and rely greatly on the attitude gyro, an instrument with which he was not completely familiar. The pitch display of this instrument is the reverse of the instrument he was accustomed to; therefore, he could have become confused and thought that he was making a climbing turn when in reality he was making a descending turn. The fact that the aircraft struck the ground in a steep turn but with the nose lowered only slightly, indicates that some control was being effected at the time. The weather briefing supplied to the pilot was seriously inadequate in that it failed to even mention adverse flying conditions which should have been highlighted.
Probable Cause
The Board determines that he probably cause of this accident was the pilot’s unwise decision to embark on a flight which would necessitate flying solely by instruments when he was not properly certificated or qualified to do so. Contributing factors were serious deficiencies in the weather briefing, and the pilot’s unfamiliarity with the instrument which determines the attitude of the aircraft.
By the Civil Aeronautics Board: James R. Dupree/ Chan Gurney/Harmar D. Denny/ G. Joseph Minetti/ Louis J. Hector